Filter Component
The Filter component allows users to interactively refine the data shown on their map and in data components. This is particularly useful when you want to enable users to explore specific subsets of data - for example, showing only certain types of locations on a map, or filtering data by date ranges.
Available Filter Types
Filters can be configured for both categorical and continuous data fields:
Categorical Fields
For fields containing discrete categories (like store types, product categories, or status values), the following filter types are available:
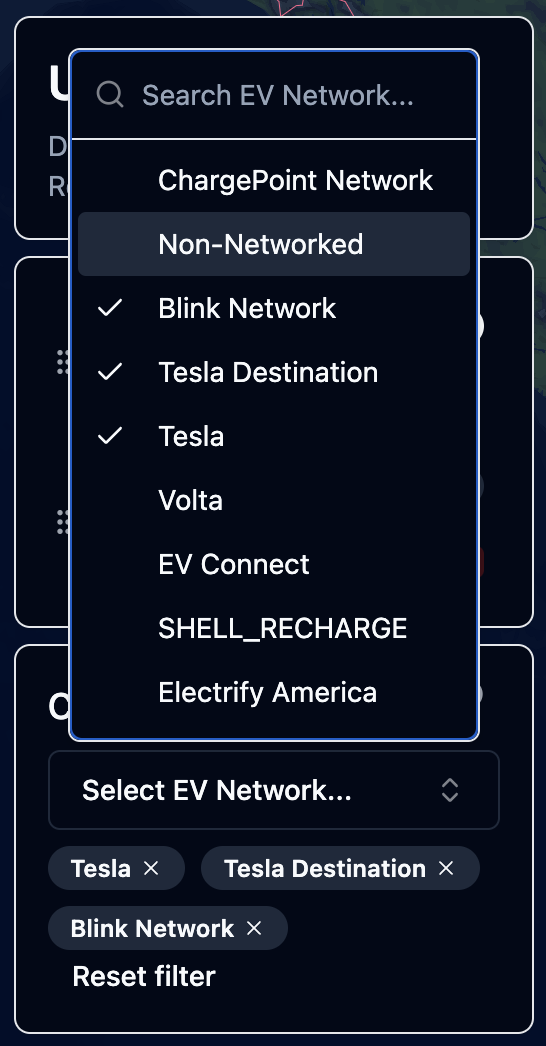
- Dropdown with Search: A searchable dropdown menu that displays all unique values
- Supports both single and multiple value selection
- Includes search functionality to easily find values in large lists
- Best when users need to browse available values
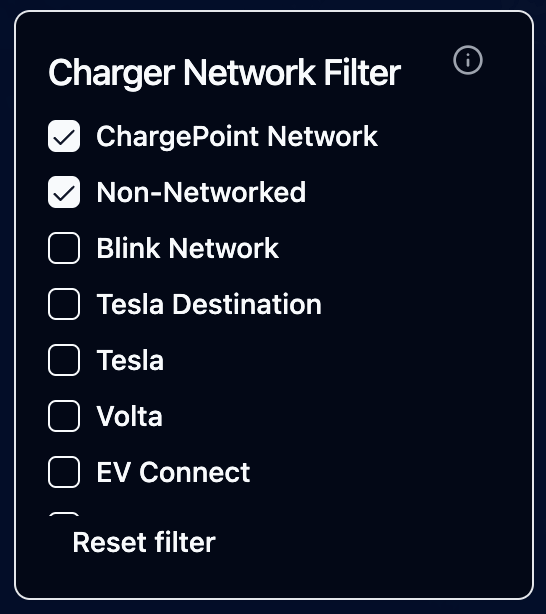
- Radio/Checkbox Buttons: Display all options as clickable buttons
- Radio buttons for single selection
- Checkboxes when multiple selection is enabled
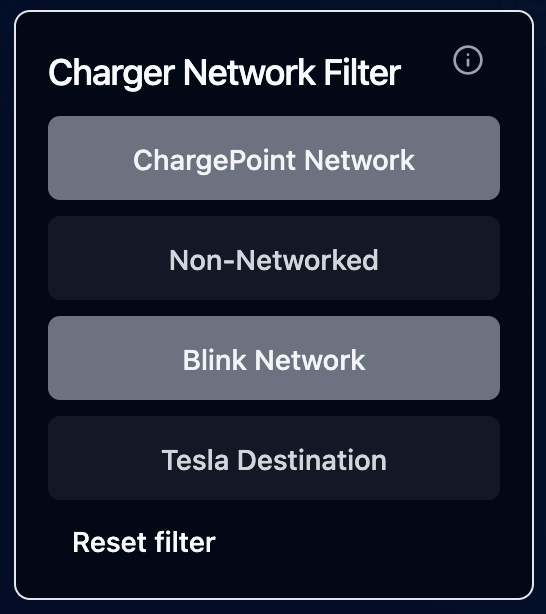
- Toggle Switches: Display options as toggle switches
- Best for categorical fields with a small number of options
- Supports both single and multiple selection
Text/ID Fields
For text fields, numeric IDs, or H3 fields where you want to filter for specific known values:
- Text Filter: Manual text input for filtering specific values
- Supports single or multiple value selection
- Users type specific values to filter for (e.g., order IDs, tracking numbers)
- Best when you know the specific value(s) you're looking for
- Case-insensitive matching
- Special H3 capabilities: When filtering on H3 fields, automatically includes child cells for hierarchical filtering
When to use Text Filter vs. Dropdown:
Use Text Filter when:
- You know specific values you're looking for
- The field has too many unique values for a dropdown
- Filtering for IDs or codes that are easier to type than select
- Need H3 hierarchical filtering capabilities
Use Dropdown when:
- Users need to browse available values
- Manageable number of unique values (< 100)
- Users may not know what values are available
Continuous Fields
For numeric fields (like prices, distances, or timestamps), two slider types are available:
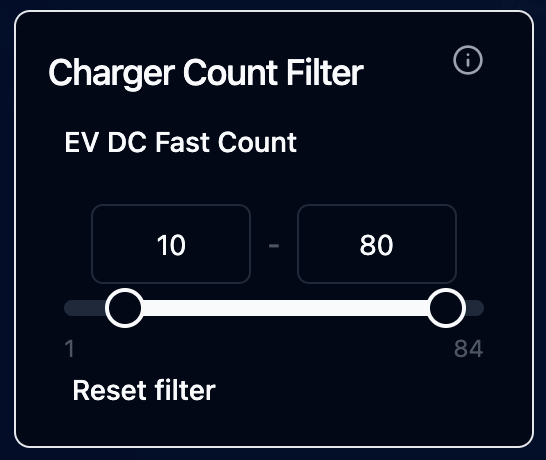
- Range Slider: Select a minimum and maximum value
- Useful for filtering numeric ranges (e.g., "show prices between $10 and $50")
- Single Value Slider: Select a single threshold value
- Useful for filtering above or below a specific value
The text filter can also be used with continuous fields, for filtering for a specific value
Adding and Configuring Filters
- Open the Edit Map sidebar and navigate to the "Components" tab
- Click "Add Component" and select "Filter"
- Configure the following settings:
- Data Source: Select the data source containing the field to filter
- Field: Choose the field to filter on
- Filter Type: Select the appropriate filter type (options vary based on field type)
- Allow Multiple Selections: Enable/disable multiple value selection (for categorical filters)
- Title & Description: Add optional explanatory text
- Apply to Layers: Select which map layers and data components this filter should affect
Applying Filters to Layers and Components
Each filter can be configured to affect specific map layers and data components. When configuring a filter, you can select from:
- Any map layer using the same data source
- Data components (Big Numbers, Bar Charts, Histograms) using the same data source
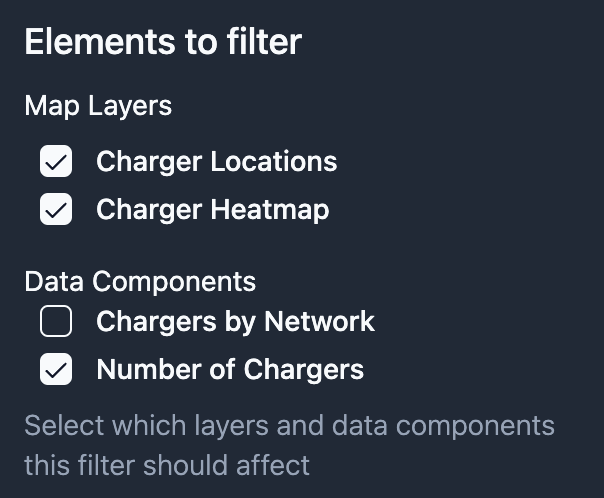
This allows you to create focused filters that only affect relevant visualizations on your map.
Saving Filter States
When you save a map that includes filters:
- The filter configuration (type, field, affected layers) is saved
- The current filter selection (selected values or ranges) is preserved
- Users who load the map will see the same filtered view
- Users can modify filter selections even in read-only mode
H3 Hierarchical Filtering
When using a Text Filter on an H3 field, special hierarchical filtering capabilities are automatically enabled.
How H3 Hierarchical Filtering Works
The H3 geospatial indexing system is hierarchical - each H3 cell at a given resolution contains multiple child cells at higher (more detailed) resolutions. Text filters on H3 fields automatically handle this hierarchy:
- If you enter an H3 cell identifier, the filter checks its resolution
- If the H3 cell is at a lower resolution (coarser) than the H3 field in your data, the filter automatically includes all child cells
- If the resolution matches or is higher, it filters for exact matches
Example:
If your dataset contains H3 cells at resolution 9 (city block level), and you filter for an H3 cell at resolution 7 (neighborhood level):
- The filter will show all resolution 9 cells that are children of the resolution 7 cell
- This effectively filters for a larger geographic area by specifying a single parent cell
H3 Format Support
Text filters accept H3 cells in hexadecimal format:
- Example:
8c275268836d3ff(hexadecimal string) - Both uppercase and lowercase hexadecimal values are supported
Best Practices
- Use descriptive titles and descriptions to help users understand what they're filtering
- Consider the number of unique values when choosing a filter type:
- Text filters work best for known specific values or IDs
- Dropdowns work well for browsing available categories
- Radio buttons and toggles are better for fewer options (< 10)
- Sliders are ideal for continuous numeric ranges
- For text filters, provide examples of valid values in the description
- For H3 text filters, explain that users can enter cells at different resolutions
- Remember that filters affect both the map and any selected data components
- Multiple filters can be combined to create complex queries
- Enable multiple selections when users might need to filter for several related values
Examples
Here are some common use cases for filters:
Categorical Filters:
- Filtering points-of-interest by category (restaurant, retail, service)
- Filtering sales data by product type
- Filtering orders by status (pending, shipped, delivered)
Continuous Filters:
- Showing only high-value transactions above a threshold
- Filtering properties within a specific price range
- Displaying deliveries within a certain distance
Text Filters:
- Finding specific order IDs or tracking numbers
- Filtering for multiple store IDs to analyze specific locations
- Filtering for specific customer account numbers
H3 Text Filters:
- Filter data at street level (resolution 12) by entering neighborhood cells (resolution 8)
- Enter a resolution 6 H3 cell to see all resolution 9 cells within that metro area
- Flexible geographic filtering without pre-aggregating data